What Is the Model Context Protocol?
MCP (Model Context Protocol) is an open-source standard for connecting AI applications to external systems.
Using MCP, AI applications like Claude or ChatGPT can connect to data sources (e.g. local files, databases), tools (e.g. search engines, calculators) and workflows (e.g. specialized prompts)—enabling them to access key information and perform tasks.
Think of MCP like a USB-C port for AI applications. Just as USB-C provides a standardized way to connect electronic devices, MCP provides a standardized way to connect AI applications to external systems.
Source: Model Context Protocol
Main Concepts
Transport layer
The transport layer manages communication channels and authentication between clients and servers. It handles connection establishment, message framing, and secure communication between MCP participants.
MCP supports two transport mechanisms:
- Stdio transport: Uses standard input/output streams for direct process communication between local processes on the same machine, providing optimal performance with no network overhead.
- Streamable HTTP transport: Uses HTTP POST for client-to-server messages with optional Server-Sent Events for streaming capabilities. This transport enables remote server communication and supports standard HTTP authentication methods including bearer tokens, API keys, and custom headers. MCP recommends using OAuth to obtain authentication tokens.
Primitives
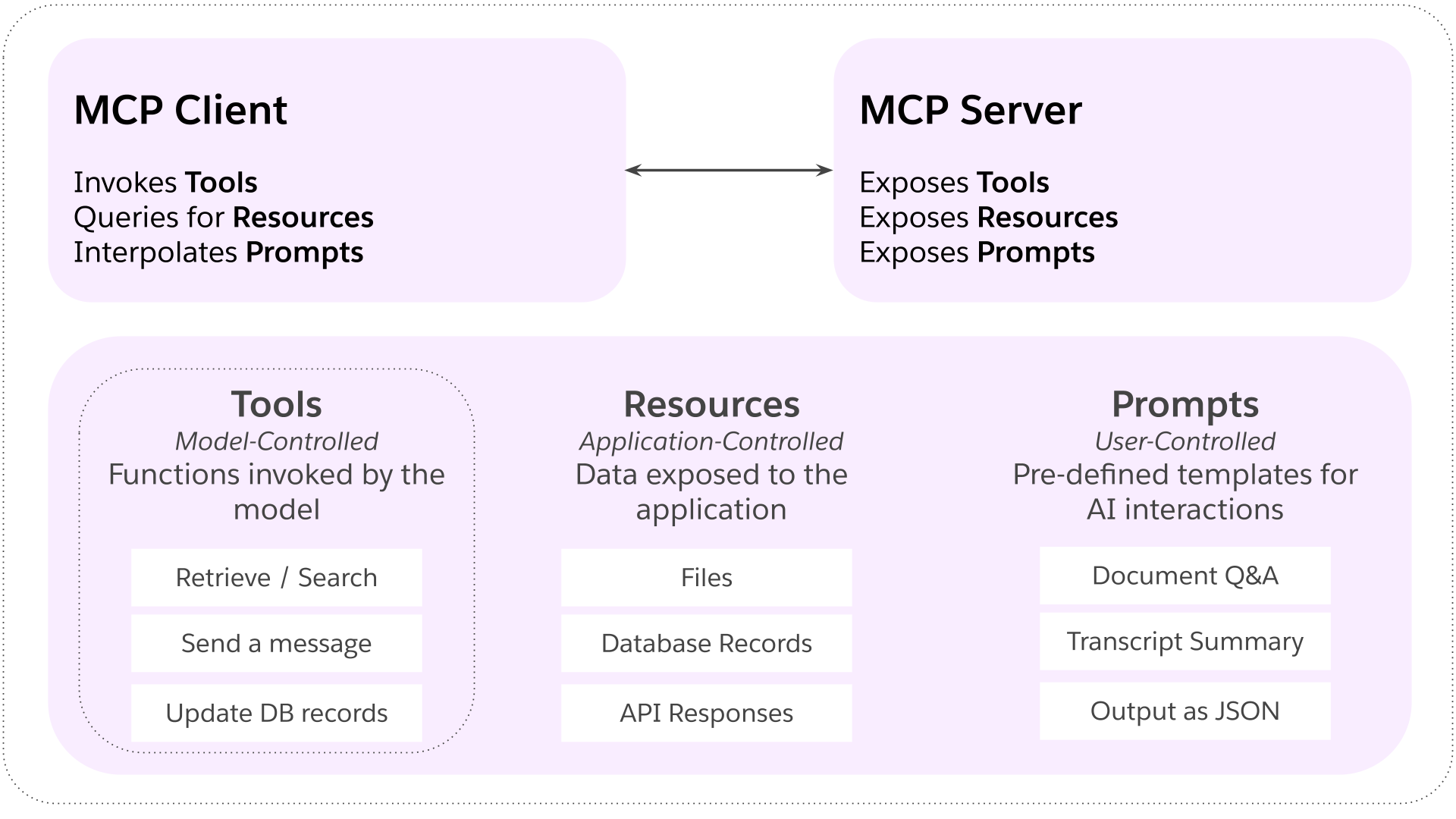
MCP primitives are the most important concept within MCP. They define what clients and servers can offer each other. These primitives specify the types of contextual information that can be shared with AI applications and the range of actions that can be performed.
MCP defines three core primitives that servers can expose:
- Tools: Executable functions that AI applications can invoke to perform actions (e.g., file operations, API calls, database queries)
- Resources: Data sources that provide contextual information to AI applications (e.g., file contents, database records, API responses)
- Prompts: Reusable templates that help structure interactions with language models (e.g., system prompts, few-shot examples)
Source: Model Context Protocol